- Is AI bound to take over the music industry?
- The music-generating capabilities of algorithms
- Composers use AI to create songs
- AI-powered mastering and talent spotting
- Unclear legal status of AI-generated music
- Why the music industry needs to embrace AI
The music industry is no stranger to disruption. From CDs and Napster to iTunes and Spotify, studios and artists have adapted to many different trends. And their skills are being tested once again, as new technologies threaten to make musicians obsolete. Artificial intelligence (AI) is now taking the stage and acting as both a music composer and performer. Algorithms create techno and death metal songs, drum patterns, and new melodies that spark creativity in singers. And although the copyright status of AI-generated music remains unclear, machines are likely to play an even larger role in people’s creative endeavors in the future.
Is AI bound to take over the music industry?
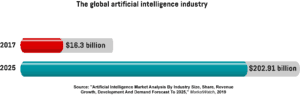
The music industry veteran Scott Cohen famously observed that “Every ten years something kills the music industry. If you want to know what’s next look at the tech world. “With 70 per cent of firms adopting at least one AI technology by 2030, it’s clear that algorithms are a major disruptive force in today’s economy and are set to become a $ 202.91-billion -worth market by 2025, growing from just $ 16.3 billion in 2017. Streaming services like Deezer already use AI to sort thousands of tracks and provide users with personalized recommendations. And in the future, advanced technologies will fuel the growth of the music industry and change the way songs are composed and delivered.
The music-generating capabilities of algorithms
San Francisco, for instance, is home to the Algorithmic Art Assembly, a festival that features performers who use software to generate music. Instead of mixers and turntables, DJs entertain guests by writing code that creates sounds and beats, and the software is projected onto the wall for everyone to see. These parties, called algorithaves, are increasingly popular in the city, which is full of engineers and developers that appreciate DJs with coding skills. And the music created by AI doesn’t sound too different from typical live electronic beats played in raves around the world.
Algorithms are also used to eliminate “humans from black metal”, as musicians and technologists CJ Carr and Zack Zukowski say . The duo developed an AI program called Dadabots that’s initially fed with songs from metal groups like Aepoch, Battles, and Meshuggah. Then, the algorithm identifies the most frequent musical elements and sequences and produces samples of death metal music. The program streams new audio content nonstop on its YouTube channel. And while much of the produced music is gibberish with no room for breaths and super-fast guitar riffs, an untrained ear would find Dadabots a convincing band. “While we set out to achieve a realistic recreation of the original data, we were delighted by the aesthetic merit of its imperfections,” they say. “Solo vocalists become a lush choir of ghostly voices, rock bands become crunchy cubist-jazz, and cross-breeds or multiple recordings become a surrealist chimera of sound.” Carr and Zukowski have released ten different AI-generated albums so far, and they plan to further refine their software.
And Sony has developed a smart algorithm called DrumNet that adds kick-drum beats to songs. Users can decide whether to manually set the music style or let the AI extract a style from some popular song and add it to the newly created pieces. The research team used 665 pop, rock, and hip-hop tracks to train the software to spot patterns of how drums are used in relation to other instruments.
Other music-making platforms are equally more powerful. Amper, for instance, enables users to simply pick a genre and a mood, and the AI then creates a relevant instrumental song. The audio file can then be further modified by adding or removing certain instruments or changing the tempo or mood of the song. People can produce songs without knowing anything about music theory or composition, which essentially levels the playing field in the creative industry and enables many more people to make music. Amper’s co-founder, Michael Hobe, says that AI is “allowing more people to be creative and then allowing the people who already have some of these creative aspects to really further themselves.”
Composers use AI to create songs
Musicians don’t shy away from using smart algorithms to produce better content. Taryn Southern, an American singer and songwriter, uses AI tools such as Amper, IBM Watson Beat, and Google Magenta to generate percussion, melodies, and chords. She then edits the AI-generated music, writes lyrics, and performs the vocals. Southern explains that she knows little about music theory and the software helps her overcome that obstacle. And many other musicians use AI to create enchanting music, despite not having the resources of well-known studios.
The French composer Benoît Carré also relies on AI tools to create music. He used Sony’s algorithm called Flow Machines to produce several songs, ranging from pop pieces to folk ballads. The software was first provided with songs from a specific genre, and then it generated unique melodies that were further edited by the team. Carré released all of the songs in the Hello World album, and most listeners would hardly notice that the music is AI-generated. But algorithms still require human experts that “stitch the songs together, give them structure and emotion”, Carré explains , adding that AI is far from replacing musicians.
One of the co-producers in the Hello World project is Michael Lovett from the electronic band NZCA Lines. He wrote the Multi Mega Fortune song for the album, feeding Flow Machines with various songs. The AI then released up to 10 short melodies at a time, and Lovett would analyze those to find tunes he liked. And as the process continued, he eventually stitched enough melodies together to create the song. Unlike Carré, Lovett is scared that AI might replace musicians, and he says that “Hopefully I’m not in 20 years one of those people who has been responsible for the downfall of creative music.”
AI-powered mastering and talent spotting
Apart from generating music, algorithms are changing the industry in other ways as well. For example, the software firm LANDR provides musicians with an affordable mastering service that’s critical for producing a clean master copy of a song, ensuring the file is optimized for distribution on multiple formats like CDs and streaming platforms like Spotify and SoundCloud. The process also fixes any mistakes missed in the final mix. Human-based mastering is expensive for many aspiring musicians, which is why LANDR’s AI-powered software has been used by more than two million musicians to master around 10 million songs.
Meanwhile, the Warner Music Group has acquired the tech startup Sodatone that develops talent-spotting algorithms and predicts a song’s commercial potential. Clearly, finding the next Beyoncé or U2 will take both an artistic ear and data-driven programs. And the streaming giant Spotify is well-known for using AI to provide customers with personalized recommendations. Its curated music lists such as Discover Weekly help fans to find songs they like among thousands of pieces uploaded to the platform every day.
Unclear legal status of AI-generated music
AI has many applications in the music industry, and both artists and studios benefit from technological progress. But the use of algorithms in music production is limited by several obstacles. For one, AI is still far from independently creating complex music that convincingly sounds human-made. It doesn’t take much before listeners spot that something isn’t right. Margaret Skull, a composer and cellist, says that “Music is so complicated. It has so many dimensions that if you get one part of it wrong, people are just like, ‘Eugh!’. ”
And even if algorithms eventually produce Grammy-winning tracks without any human touch, legal challenges will arise. For instance, who owns the copyright in AI-generated musical work – machines or engineers? And what about artists whose songs were used to train the algorithms? Do they need to be compensated in some way, as the AI couldn’t produce a song without analyzing existing tracks? And how can anyone even prove which songs were used to train the neural network? Courts are unlikely to allow outsiders access to proprietary algorithms, and only deep-pocketed studios could sustain the legal fight. Many of these questions remain unanswered as legal systems across the world are yet to tackle the issue of AI-generated music.
And this uncertainty forced some companies to be creative. For example, the developers of Endel, an app that uses AI to generate personalized ambient ‘soundscapes’, signed a distribution deal with Warner Music and then had to provide details on how to credit each track. The company decided to list all six employees as songwriters for more than 600 tracks, even though none of them know how to write or compose a song. But obtaining copyright on AI-generated music is essential if developers are to have incentive to keep innovating in this field.
Why the music industry needs to embrace AI
Smart algorithms enable the music industry to explore new ways of creating songs. AI can now generate music, while advanced platforms provide musicians with mastering capabilities previously available only to major studios. And although people worry that technology might replace musicians and bands, the more likely scenario is that AI will augment our creativity. The mixture of human and machine intelligence will lead to exciting creative projects that otherwise might never happen. And that in itself is sufficient reason for the music industry to embrace AI.
Share via:


